The Ratnas of Samudra Manthan
- May 14, 2021


The Ratnas of Samudra Manthan
- May 14, 2021
By Shivam Pathania
Samudra Manthan or the churning of the ocean is one unique occasion when the Devas and their arch-nemesis, the Asuras, unite for an important reason. The churning of the ocean was a result of a curse by Sage Durvasa. Once, he offered a garland to Indra, the king of Devas. Indra accepted the garland and showed his happiness, putting the garland on his elephant, Airavata, as an ornament. Airavata, irritated by the scent of the garland, picked it with his trunk and threw it on the ground. Durvasa was furious and cursed Indra and the devas to lose their kingdom, power, and glory.
As a result, Indra’s mighty vahana instantly went into oblivion. Lakshmi, the goddess of fortune, could no longer stay in the same realm as the Devas, and parted ways with her consort, Vishnu. She made the depths of Kshir Sagar her new home. Due to Lakshmi’s absence in Devlok, the devas lost all their riches. The luminous Chandra, adorning Shiva’s matted hair, disappeared too. Robbed of their power, the devas were soon defeated by the asuras in battle. The defeated devas approached Lord Vishnu for a solution, who advised them to churn Kshir Sagar, to obtain Amrit. Amrit or the elixir of immortality would help the devas regain their powers. The Asuras willingly offered to assist their half-brothers since they too wanted immortality and invincible powers by consuming Amrit.
To receive more such stories in your Inbox & WhatsApp, Please share your Email and Mobile number.
Mount Mandara was used to churn the ocean, which was kept afloat in the ocean by Kurma, Vishnu’s turtle avatar. The Naga king, Vasuki, who Shiva wears as a garland, became the churning rope. Several precious items, ratnas, emerged from the cosmic ocean which were distributed amongst the Devas, the Asuras and the Sages.
Halahala
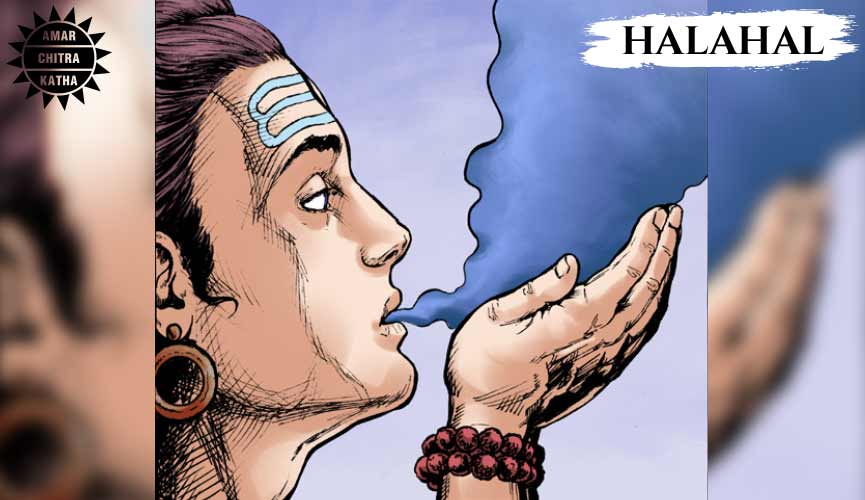

The Halahala was a deadly poison that had the potential to destroy all beings in the three realms. None amongst the armies of asuras and devas stepped in to stop the poison from spreading into the universe as they feared the poison would destroy them too. Lord Shiva descended from Mount Kailash to consume the poison. Goddess Parvati, Shiva’s consort, used her powers to stop the Halahal in Shiva’s throat, and as a result, his throat turned blue. Thus he came to be called Neelkanth.
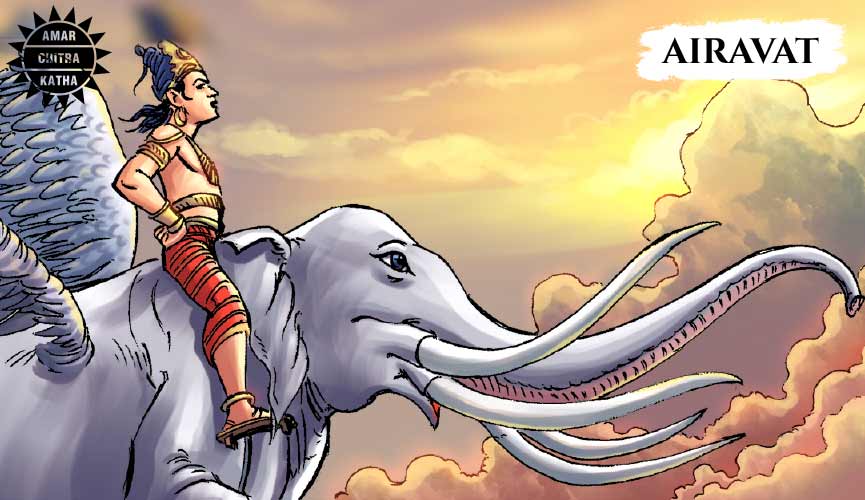
Airavata
Airavata, the king of elephants, was a white coloured winged being with six trunks and six pairs of tusks. He said to dig his trunk deep into the ground and reach water which is inaccessible to humans. He uses his trunk to spray the water in the form of monsoon showers. After appearing from the cosmic ocean, Airavata chose to serve his master Indra, who was delighted to reunite with his loyal vahana.
Uchhaisravas
Often considered as the king of the horses, the seven-headed, snow-white horse, was one of the three animals that appeared during the Samudra Manthan. The magnificent steed was taken by Indra. Eventually, Uchhaisravas came into the hands of King Mahabali, the asura king, who ruled over the three worlds.
Once Goddess Lakshmi was spellbound by the beauty of Uchhaisravas and forgot to pay attention to her consort, Vishnu. This infuriated him and he cursed Lakshmi to be born as a mare.
The colour of Uchhaisravas’ tail once became a topic of debate for two sisters, Kadru and Vinata. The sisters studied the horse from a distance and Vinata declared that the horse’s tail was white, while Kadru insisted that the tail was black. The sisters decided to come back and see the horse the next day. Whoever of the two had guessed the wrong colour, would have to become the slave of the other. Kadru won the bet by treachery as she commanded her sons, the Nagas, to cover the tail of the horse. Thus Vinata ended up becoming Kadru’s slave.
Kamdhenu
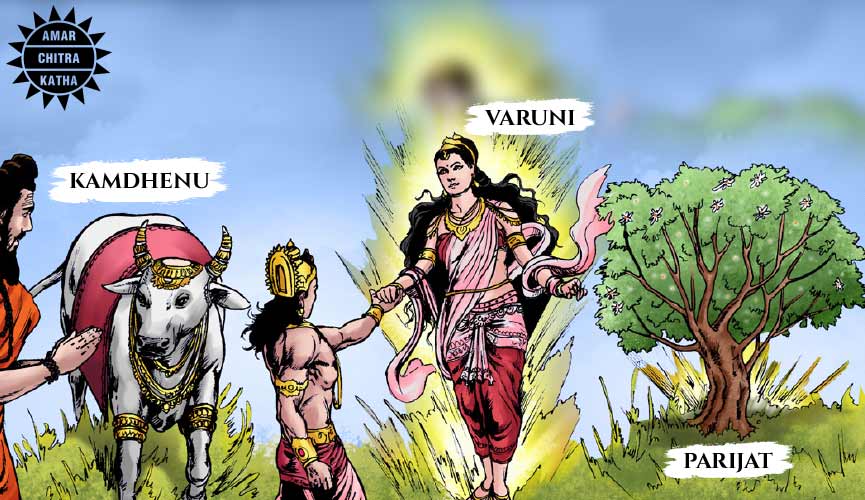

Kamdhenu was one of the precious ratnas obtained from the cosmic ocean and is considered to be the mother of all cattle. Kamdhenu is depicted with the face of a woman, the body of a cow with a pair of wings and the tail of a peacock. She was given to the Saptrishis as she provided them with ample milk. The milk was used to prepare curd and ghee which were regularly required for their sacred rituals. According to the Mahabharata, Kamdhenu was in the possession of one of the Saptrishis, Jamadagni. The sage invited King Kartavirya Arjuna to a feast. The greedy king learnt about the resourcefulness of Kamdhenu and forcefully took Kamdhenu and her calf away from the sage. The sage’s son, Parshurama, the sixth avatar or incarnation of Vishnu, single-handedly defeated the king and his army, successfully retrieving the sacred cow and her calf.
Apsaras
Apsaras are female heavenly spirits of Devaloka or the home of the gods. They are associated with music and dance. After appearing from the cosmic ocean, they chose Gandharvas as their companions. The Gandharvas served as musicians in Indra’s court. Indra, who was constantly insecure about his throne, often commanded the enchanting apsaras to distract sages or asuras from their tapasya to achieve his own ends.
Parijat
From the depths of the ocean, sprung a divine flowering tree called the Parijat. The flowers of the tree were white, with a tinge of orange at the stalk. Indra decided to keep the beautiful flowering tree with the enchanting fragrance for himself and planted the tree in his garden in Devaloka. Yugas later, Krishna and Indra duelled over the tree as Krishna wanted to bring the tree bearing the scented flowers to Prithvilok for his wives Satyabhama and Rukmini. Eventually, Krishna defeated Indra, and took the tree. The tree has a special significance in Hinduism, as it is forbidden to pluck its flowers and only the fallen flowers can be used to worship deities.
Vishnu’s Sharanga bow, Panchajanya Conch, and Kaustubh Mani
The Sharanga bow was one of the two divine bows crafted by Vishwakarma, the architect of the gods. Vishnu used the bow in his Parshurama, Rama and Krishna avatars. Before returning back to his holy abode, Vishnu, in the form of Krishna, left the bow in the possession of Varuna, the god of oceans.
In ancient times the sound of the conch signified the beginning of a war. Vishnu’s conch, Panchajanya is a symbolic way of portraying his role as the preserver of the universe. God steps into battlefields again and again, in different avatars to save humanity.
Kaustubh Mani is a sacred precious gemstone that is embedded in the necklace worn by Vishnu. The gemstone is said to be as beautiful as an exotic lotus and as radiant as the sun.
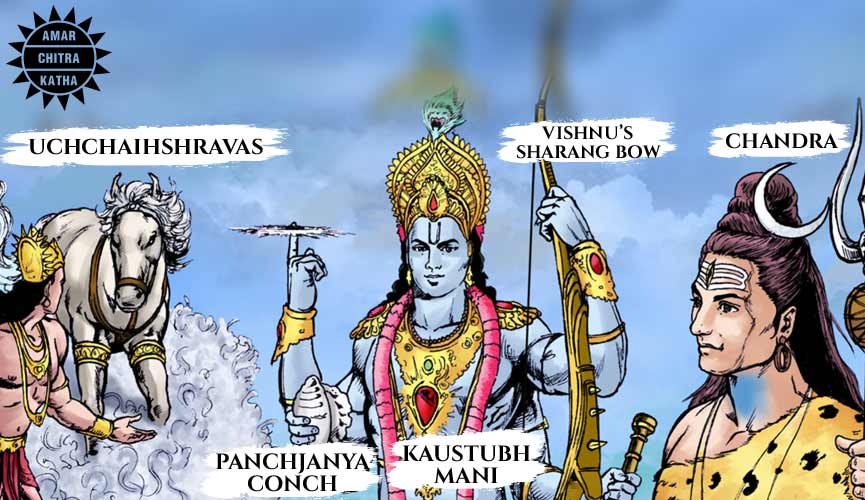
Chandra
The moon God Chandra appeared as one of the precious ratnas and took refuge in the matted hair of Shiva. His father-in-law, Prajapati Daksha once cursed him for not being a good husband to his daughters. Due to the curse, Chandra lost his powers and his body started withering. After extensive prayers, Shiva came to the deity’s rescue and wore him as an ornament in his hair to neutralize the curse. However, Chandra still waxes and wanes as a result of that curse.
Lakshmi and Alakshmi
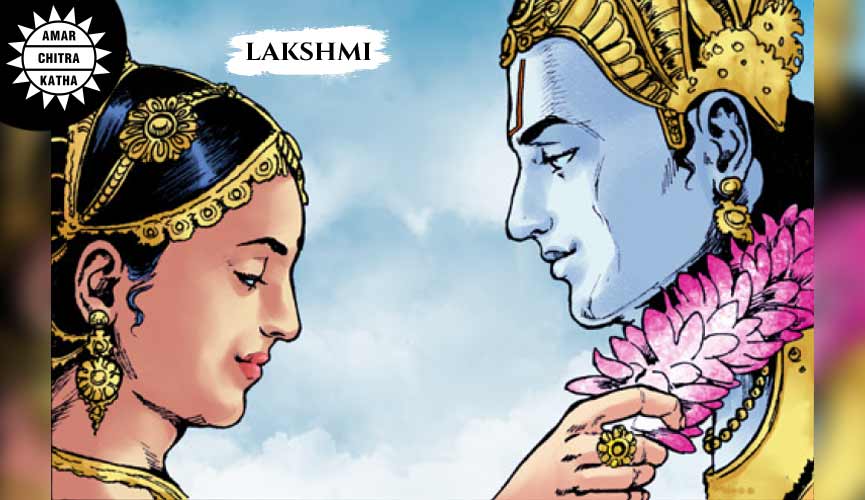

Lakshmi is the goddess of wealth, prosperity and fortune. She is one of the three supreme goddesses, with Saraswati and Parvati. She emerged from the cosmic ocean draped in her red and gold saree while seated on a grand lotus with smaller lotuses in her hands. After a long time of separation, the goddess was finally reunited with her consort, Lord Vishnu. Her return brought back the riches of the devas, giving Devaloka its earlier splendour.
The arrival of Lakshmi was followed by her counterpart and elder sister, Alakshmi, who had unkempt hair and was draped in a single white cloth. She is the goddess of misfortune, poverty and misery and is said to visit houses filled with ego, pride, selfishness, and envy. Unlike her sister Lakshmi, who likes sweet food, Alakshmi has an appetite for hot, sour and pungent food. So, many Hindu households often hang lemon and chillies at their doorstep to satisfy the appetite of the goddess of misfortune.
Dhanvantri
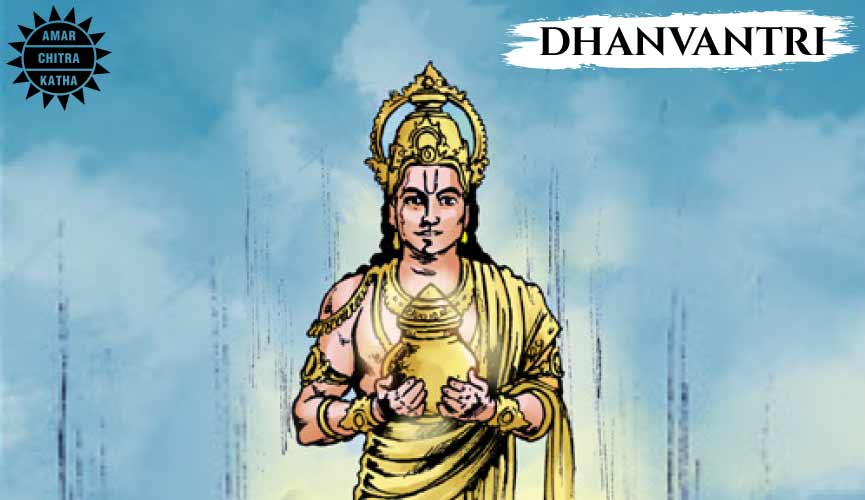

Dhanvantri, the physician of the gods, appeared from the turbulent ocean carrying the pot of Amrita. Dhanvantri was responsible for teaching the ancient knowledge of medical science, Ayurveda, to mortals. Brahma created Ayurveda, before he created mankind, but the vast knowledge of medical science was difficult for mortals to understand. So, Dhanvantri split the original text into eight divisions and taught his disciples.
Amrita
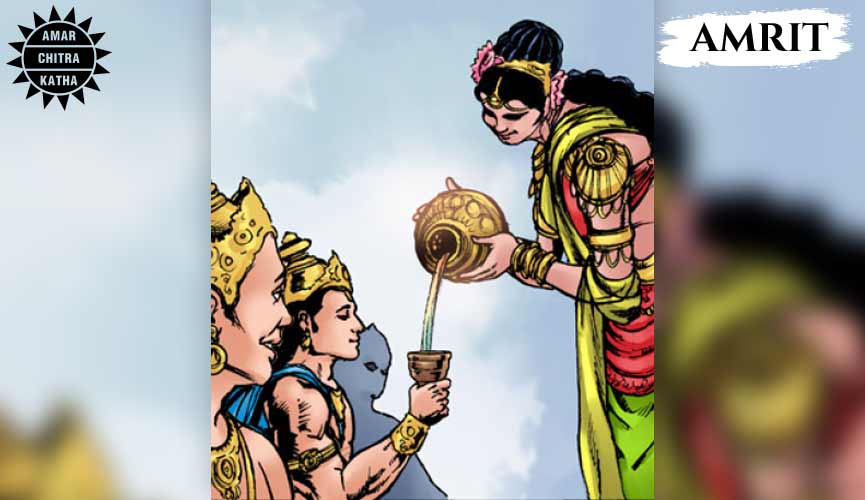

As soon as Dhanvantri appeared with the pot of Amrit, the Asuras snatched the pot and planned to consume the entire pot of elixir. Vishnu devised a plan and took the form of an enchanting woman, Mohini. Mohini used her charm to lure the asuras out of hiding and used the opportunity to take the pot back to the Devas. While the devas were consuming the elixir to regain their divine strength back, one of the asuras, Rahuketu disguised himself as a deva to taste the Amrit. However, he was discovered just as he was pouring the liquid into his mouth. Vishnu instantly hurled the Sudarshan Chakra and beheaded Rahuketu but the amrita had already reached the asura’s throat. Rahuketu’s head and body were flung on opposite sides of the universe and became Rahu and Ketu.
To receive more such stories in your Inbox & WhatsApp, Please share your Email and Mobile number.

Comic of The Month
The Naval Journey of India Book I
This book is the first of a three-book series that takes a deep and detailed look at India's Naval History and a deep insight into the lives of our men and women in white. But any series on the Indian Navy has to start at the very beginning - exploring India's celebrated maritime history. Join our little hero, Bharat, and his grandfather, Commodore Sagar, as they sail into the deep blue waters of time. Book I of The Naval Journey of India takes a sweeping look at India's maritime endeavours, how the seas impacted us over millennia and how the oceans made us who we are.